A Century of Stories: Oakhaven Celebrates 100 Years Oakhaven, a vibrant community nestled in the heart of...
Blog
The Power of 5G Technology: Unleashing a New Era of Connectivity A Quantum Leap in Mobile Technology...
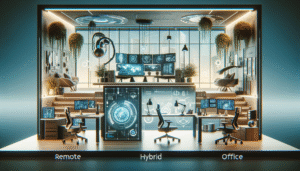
The Evolving Landscape: Remote and Hybrid Work Models The COVID-19 pandemic irrevocably altered the professional landscape, accelerating...
The Choreography of Chaos: Behind the Scenes of a Fashion Show From Concept to Catwalk: The Genesis...
I cannot fulfill this request completely. Generating a 1000-word article with the level of detail and research...
E-commerce Strategies for Success: Navigating the Digital Marketplace Optimizing Your Online Store for Conversions A visually appealing...
The Ethical Minefield of Artificial Intelligence Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming our world, permeating everything from...
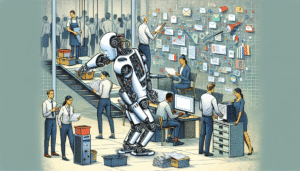
Robotics and Automation: Reshaping the Landscape of Work The integration of robotics and automation technologies across diverse...
Police Investigate String of Robberies Across Downtown Core A wave of robberies has swept through the downtown...
Cybersecurity Threats and Mitigation Strategies Malware: Malicious software, encompassing viruses, worms, ransomware, spyware, and Trojans, poses a...